India-Oman have always been bridged by enormous goodwill. Archaeological excavations in Oman have unearthed evidence to show Indo-Oman trade during the Classical Age dated to circa third century BCE. Later, Oman had links with the Indian states in Gujarat and along the Malabar Coast.
History books say that the Indian prince Tipu Sultan sent a diplomatic delegation to Oman during his reign. Trade between India and Oman has a history of several millenniums.
Today, there are around 3000 joint ventures between Indian and Omani partners in Oman with a total investment of around $7.5 billion.
Indians in Oman
Oman is home to a large Indian expatriate community and for Oman India is an important trading partner. Oman has over five hundred thousand Indian nationals living there making them the largest expatriate community in Oman.
They annually remit around $780 million to India. India is a major destination for Omani students pursuing higher studies and in recent years there have been increasing numbers of medical tourists coming into the country from Oman.
Oman has also been trying to promote itself as a tourist destination in India. Annually, over 12,000 Indians visit Oman on tourist visas.
Economic Relations
Oman is politically stable and prosperous with a state-of-the-art and growing infrastructure. Oman has a robust oil-based economy which is being judiciously diversified to other areas like tourism, agriculture & fisheries, SMEs, and investments abroad.
Among the Indian financial institutions, State Bank of India, Bank of Baroda, HDFC Ltd and ICICI Securities; in the Public Sector Undertakings, Air India, Air India Express, Life Insurance Corporation (LIC), New India Assurance Co., Telecommunications Consultants India Ltd. (TCIL), Engineers India Ltd. (EIL) , Engineering Projects India Limited (EPIL) and National Building Construction Company (NBCC) have presence in Oman.
Wipro, L&T, Shapoorji Pallonji, Jindal, Aditya Birla Group, Nagarjuna Construction Company, Simplex, KEC International are some of the private sector companies engaged in various projects.
Indian and Omani firms have undertaken joint ventures in a wide range of sectors including fertilisers, pharmaceuticals, energy and engineering. The Oman-India Fertiliser Company (OMIFCO) plants at Sur in Oman and the Bharat-Oman Oil Refinery at Bina have been set up as joint ventures between Indian public sector companies and Oman Oil Company.
The India-Oman Joint Investment Fund, a private equity fund backed by the State General Reserve Fund of Oman (SGRF) and State Bank of India (SBI) began operations in 2011 and the initial seed capital of $100 million has been
utilised.
Gas Pipeline Co-operation India has been considering the construction of a 1,100-km-long underwater natural gas pipeline from Oman. Called the South Asia Gas Enterprise (SAGE), it will act as an alternative to the Iran–Pakistan–India pipeline.
Defence Co-operation
 Oman is the first Gulf nation to have formalised defence relations with India. Both countries conducted joint military exercises in 2006 and subsequently signed a defence agreement. The Indian Navy has berthing rights in Oman, and has been utilising Oman’s ports as bases for conducting anti-piracy operations in the Gulf of Aden.
Oman is the first Gulf nation to have formalised defence relations with India. Both countries conducted joint military exercises in 2006 and subsequently signed a defence agreement. The Indian Navy has berthing rights in Oman, and has been utilising Oman’s ports as bases for conducting anti-piracy operations in the Gulf of Aden.
The Indian Air Force has also been holding biannual joint exercises with the Royal Air Force of Oman since 2009. Oman has approached India in order to fence along the Oman-Yemen border in order to protect the nation from growing unrest in Yemen. The standard issue rifle of the Royal Army of Oman is India’s INSAS rifle. Indian Defence Minister Manohar Parrikar’s visit to the sultanate in May 2016, during which New Delhi and Muscat signed pacts to bolster defense and security relations, underscored the important role Oman plays in India’s long-term quest to consolidate geo-economic influence and strategic clout in the greater Middle East.
The strategic cooperation between the two countries has become essential for safeguarding the waterways, with Oman proving to be an exceptionally reliable and close friend of India in supporting operations with ships and aircraft within the region. India clearly sees itself as a stakeholder in Oman’s security and cohesion.
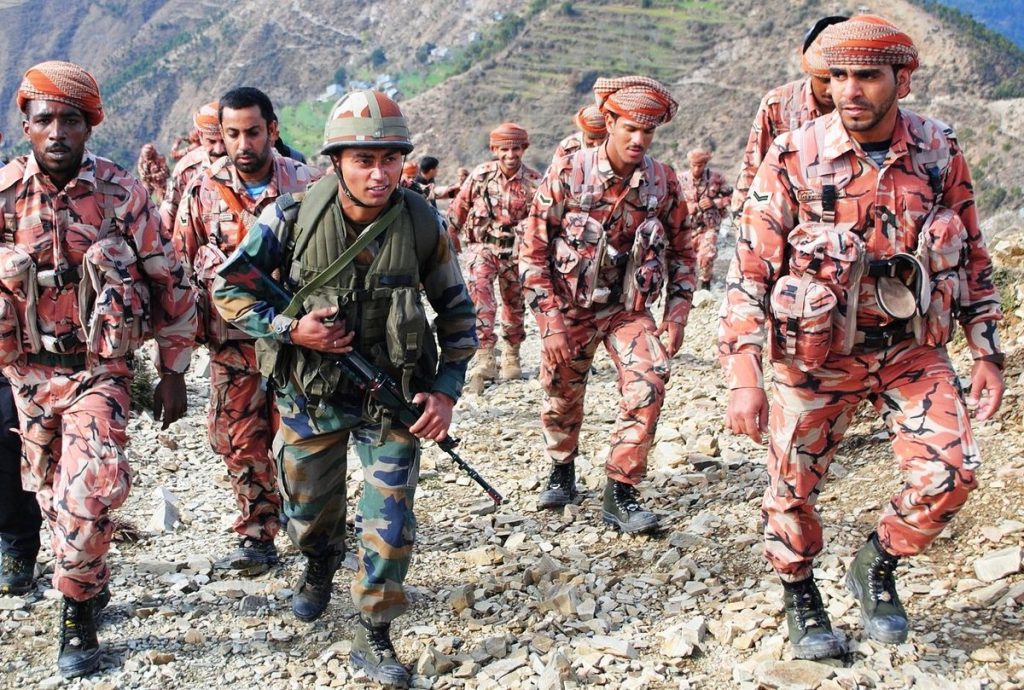 Joint Military Exercises
Joint Military Exercises
In an effort to build bilateral military to- military relations and skills, a 14- day joint defence exercise Al-Nagah-II between the armies of India and Oman was held in Himachal Pradesh in March earlier this year.
Indo-Oman Joint Army Exercise AL NAGAH-II 2017 was conducted between the Indian and Oman Army from 6 to 19 March in the Dhauladhar Ranges at Bakloh in Himachal Pradesh.
This was the second joint military exercise between the two countries which have a history of extensive cooperation in the defence arena, the first one was held in Oman in January 2015.
The participating troops for this exercise had been drawn from one infantry battalion each from the Indian Army and the Royal Army of Oman.
Approximately 60 troops from both countries participated in the exercise. In January 2016, Indian Navy and the Royal Navy of Oman conducted maritime exercise ‘Naseem al-Bahr’ in the Arabian Sea off the coast of Goa, from 22 to 26 January.